按题目思路分析后,实际上也是一个并查集的问题
- 对角线没有意义,因为是自己认识自己
- 相邻则可以合为一个并集
即:看有多少个并查集,多少个 root
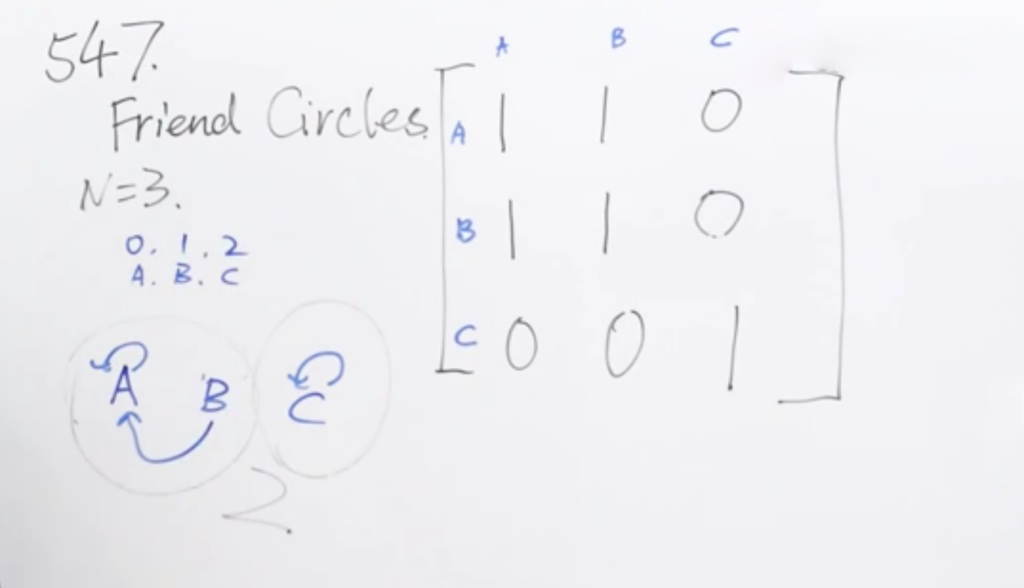
老师说与上一节的代码类似,我写了下:
class Solution {
fun findCircleNum(M: Array<IntArray>): Int {
if (M.isNullOrEmpty()) return 0
if (M[0].isEmpty()) return 0
val m = M.size
val n = M[0].size
val uf = UnionFind(M)
for (i in 0 until m) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
if (M[i][j] == 0) continue
if (M[i][j] == 1) uf.union(i, j)
}
}
return uf.count
}
class UnionFind(grid: Array<IntArray>) {
val m = grid.size
var count = 0
//初始化为自身或者初始化为-1都没关系
val parent = IntArray(m) { it }
//用于深度合并优化
val rank = IntArray(m) { 0 }
init {
for (i in 0 until m) {
parent[i] = i
count++
}
}
fun findRoot(p: Int): Int {
if (parent[p] != p) {
parent[p] = findRoot(parent[p])
}
return parent[p]
}
fun union(x: Int, y: Int) {
val rootX = findRoot(x)
val rootY = findRoot(y)
if (rootX != rootY) {
when {
rank[rootX] > rank[rootY] -> {
parent[rootY] = rootX
}
rank[rootX] > rank[rootY] -> {
parent[rootX] = rootY
}
else -> {
parent[rootY] = rootX
rank[rootX]++
}
}
count--
}
}
}
}上面的写法还可以再优化一下:因为是对称矩阵
class Solution {
fun findCircleNum(M: Array<IntArray>): Int {
if (M.isNullOrEmpty()) return 0
if (M[0].isEmpty()) return 0
val n = M.size
val uf = UnionFind(n)
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in 0 until i) {
if (M[i][j] == 0) continue
if (M[i][j] == 1) uf.union(i, j)
}
}
return uf.count
}
class UnionFind(n: Int) {
var count = 0
//初始化为本身 或者为-1都没关系
val parent = IntArray(n) { it }
//用于深度合并优化
val rank = IntArray(n) { 0 }
init {
for (i in 0 until n) {
parent[i] = i
count++
}
}
fun findRoot(p: Int): Int {
if (parent[p] != p) {
parent[p] = findRoot(parent[p])
}
return parent[p]
}
fun union(x: Int, y: Int) {
val rootX = findRoot(x)
val rootY = findRoot(y)
if (rootX != rootY) {
when {
rank[rootX] > rank[rootY] -> {
parent[rootY] = rootX
}
rank[rootX] > rank[rootY] -> {
parent[rootX] = rootY
}
else -> {
parent[rootY] = rootX
rank[rootX]++
}
}
count--
}
}
}
}发现,还是官方的这个解法看上去更简单:
官方的思路是:先来一个并查集,将parent 都填充为 -1,每联接一个元素则那个元素将不再是 -1,最后统计 -1 的个数。
并查集的大小为 N 是因为当每个人都是单独的朋友圈时最多,大小 N 个。
class Solution {
fun find(parent: IntArray, i: Int): Int {
return if (parent[i] == -1) i else find(parent, parent[i])
}
fun union(parent: IntArray, x: Int, y: Int) {
val xset = find(parent, x)
val yset = find(parent, y)
if (xset != yset) parent[xset] = yset
}
fun findCircleNum(M: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val parent = IntArray(M.size)
Arrays.fill(parent, -1)
for (i in M.indices) {
for (j in M.indices) {
if (M[i][j] == 1 && i != j) {
union(parent, i, j)
}
}
}
var count = 0
for (i in parent.indices) {
if (parent[i] == -1) count++
}
return count
}
}然后这题,DFS也是可以的:以下是官方的代码
思路是:从一个没有被访问的同学开始,找这个同学所在的行有没有认识的,有认识的话,就把这一列扫一遍,过滤掉没有被访问过的元素,同时把朋友的朋友记录下来,最后回去一开始,继续从未被访问的开始访问,每一次深度递归的开始都是一个新的朋友圈。
class Solution {
fun dfs(M: Array<IntArray>, visited: IntArray, i: Int) {
for (j in M.indices) {
if (M[i][j] == 1 && visited[j] == 0) {
visited[j] = 1
dfs(M, visited, j)
}
}
}
fun findCircleNum(M: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val visited = IntArray(M.size)
var count = 0
for (i in M.indices) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
dfs(M, visited, i)
count++
}
}
return count
}
}有 DFS 那么 BFS 也就有了。
class Solution {
fun findCircleNum(M: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val visited = IntArray(M.size)
var count = 0
val queue = LinkedList<Int>()
for (i in M.indices) {
if (visited[i] == 0) {
queue.add(i)
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
val s = queue.pop()
visited[s] = 1
for (j in M.indices) {
if (M[s][j] == 1 && visited[j] == 0) queue.add(j)
}
}
count++
}
}
return count
}
} 本站由以下主机服务商提供服务支持:
0条评论