好久好久没有玩过web啦。很多东西都过时了,也忘记了,最近不是流行Spring-boot吗?就简单的写个例子看看是如何的不一样
注:本文需要一定的j2ee基础
工程创建
打开IDEA,新建一个Gradle工程,GroupId:lckiss.com、ArtifactId:Spring-Boot,选择项目路径后一路next。
项目创建完成后,我们添加一些东西。按照官网的quick start:https://projects.spring.io/spring-boot/#quick-start
打开配置文件build.gradle,编辑内容至如下:
group 'lckiss.com'
version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:2.0.0.RELEASE")
}
}
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'eclipse'
apply plugin: 'idea'
apply plugin: 'org.springframework.boot'
apply plugin: 'io.spring.dependency-management'
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
targetCompatibility = 1.8
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
testCompile group: 'junit', name: 'junit', version: '4.12'
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web")
}
bootJar {
baseName = 'gs-spring-boot'
version = '0.1.0'
}新建一个包com.lckiss.hello,并创建一个java类HelloController,内容为:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index() {
return "Greetings from Spring Boot!";
}
}同目录下创建一个Application:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(ApplicationContext ctx) {
return args -> {
System.out.println("Let's inspect the beans provided by Spring Boot:");
String[] beanNames = ctx.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Arrays.sort(beanNames);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
System.out.println(beanName);
}
};
}
}在Application这个类旁边会有一个运行按钮,点下,控制台会输出一些日志,还有logo,并且还有端口什么的,打开浏览器,输入http://localhost:8080/,你会发现出现了Greetings from Spring Boot!字样,原因是index方法定义的url路径为/,所以返回的就是index的那个字符串了。
PS:HelloController中@RestController可以去掉,然后换成另一种风格:
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index() {
return "Greetings from Spring Boot!";
}
}
@RestController @Controller +@ResponseBody 它下面所有的方法都返回json格式
结果是一样的,你可以运行后尝试。
换种启动方式
不知道有没有注意到上面的Application写法,上面的注解是不是可以换一个?
/**
* ComponentScan扫描Controller位置
*/@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.lckiss.hello")
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}新建一个App的类,将以前的Application的类干掉,从这里启动也是可以的。但是需要注意的是,如果不在同一个包下,需要加上注解@ComponentScan(basePackages = “com.lckiss.hello”),聪明的同学会发现,后面是包名,yes,确实如此。你依旧可以尝试运行。
修改启动图标和端口号
项目创建后有一个main目录,下面有一个java和resources目录,在resources下创建两个文件一个是application.properties,还有一个是banner.txt
我的是:
.__ __ .__
| | ____ | | _|__| ______ ______
| | _/ ___\| |/ / |/ ___// ___/
| |_\ \___| <| |\___ \ \___ \
|____/\___ >__|_ \__/____ >____ >
\/ \/ \/ \/
GetStart from localhost:8080 !!!粘贴到banner.txt即可。
修改服务器端口号:
在application.properties中写入:
端口号修改 server.port=8081
重新运行下你的项目,是不端口号变成8081了。我想结果肯定是的,并且启动界面也更换了。
全局异常处理与自定义业务异常
在HelloController来模拟一下异常的发生。
/**
* 异常模拟 全局处理 可以每个都加上try catch,但是可以更简单
* http://localhost:8080/test1
* @return
*/@RequestMapping("/test1")
public String test1() {
int i=1/0;
return "Greetings from test1!";
}
/**
* 异常模拟 2 http://localhost:8080/test2
* @return
*/@RequestMapping("/test2")
public String test2() {
try {
int i=1/0;
}catch (Exception e){
}
return "Greetings from test2!";
}
/**
* 自定义业务异常模拟 2 http://localhost:8080/test3
* @return
*/@RequestMapping("/test3")
public String test3() throws BusinessException {
throw new BusinessException(500,"出错了","500异常");
}将上面的三种异常添加到HelloController中,其中第一种是未被处理的,第二种是被try,catch的,第三种是自定义的。报错先不管,继续创建一个包com.lckiss.exception,创建一个自定义的BusinessException
public class BusinessException extends Exception {
/**
* 异常处理编码
*/ private Integer code;
/**
* 异常处理信息
*/ private String msg;
/**
* 具体描述
*/ private String desc;
public BusinessException(Integer code, String msg, String desc) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
this.desc = desc;
}
public BusinessException(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
}在com.lckiss.hello包下创建一个GlobalExceptionHandler类,内容为:
/**
* @ControllerAdvice 处理Controller中所有没有被try catch包裹(比如test1方法) 的一个注解
*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
//全局异常处理(异常的类型)
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> handlerExcetion(){
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("code",500);
map.put("msg","系统繁忙,请稍候再试");
return map;
}
//自定义的业务异常处理(自定义的异常类型)
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> handlerBusinessExcetion(BusinessException businessException){
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("code",businessException.getCode());
map.put("msg",businessException.getMsg());
map.put("desc",businessException.getDesc());
return map;
}
//自定义的SQL异常处理
@ExceptionHandler(SQLException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> handlerSQLExcetion(){
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<String,Object>();
//TODO SQL异常处理逻辑
return map;
}
}写完后,去HelloController中导包,确认无错后,分别访问三种异常。
第一种返回:{
“msg”: “系统繁忙,请稍候再试”,
“code”: 500
}
第二种返回:Greetings from test2!
第三种返回:{
“msg”: “出错了”,
“code”: 500,
“desc”: “500异常”
}
聪明的你结合注释应该就明白了。当然后面的SQLException是没有可演示的,只是伪代码,别多想。
集成jsp
虽然说现在流行前后端分离,但是这个jsp,还是得演示下呀。在build.gradle中,添加一些东西,部分代码如下:
... apply plugin: 'io.spring.dependency-management' //jsp needed apply plugin: 'war'
dependencies {
....
compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web")
//jsp
compile 'org.apache.tomcat.embed:tomcat-embed-jasper'
}在application.properties中加入:
#jsp spring.mvc.view.prefix=/WEB-INF/jsp/ spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
然后创建以下目录结构:
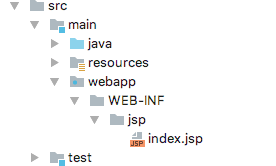
相信你不会建错,index.jsp内容很简单:
<%@ page language="java" pageEncoding="utf-8" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>title</title>
</head>
<body>
this is a SpringBoot Jsp!!!
</body>
</html>准备工作做完了,搞一个访问入口吧。在包com.lckiss.hello下新建类JspController:
@Controller
public class JspController {
/**
* @return index.jsp
*/ @RequestMapping("/jsp")
public String jsp() {
return "index";
}
}没错就是这么简单,但是注意哦,这里不是用的@RestController,所以如果你要在HelloController中创建的话,需要将RestController改为Controller,并且,返回json的加上@ResponseBody。
好了,访问下http://localhost:8080/jsp,你就会发现jsp上的内容了。如果看不到,自己找错误咯,比如路径,配置文件有没有多空格等等。
集成Mybatis与连接数据库
在application.properties中添加内容(当然,你得有一个本地的mysql数据库,这里我就不多说了):
#sql连接 spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/你创建的数据库名?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 spring.datasource.username = 你的用户名 spring.datasource.password = 你的密码 spring.datasource.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #驱动名称不必改变 除非你换了其他数据库
添加gradle依赖,在build.,gradle这个位置中添加:
......
//jsp
compile 'org.apache.tomcat.embed:tomcat-embed-jasper'
//配置mybatis
compile("org.mybatis.spring.boot:mybatis-spring-boot-starter:1.3.2")
compile("org.mybatis.spring.boot:mybatis-spring-boot-starter-test:1.3.2")
//mysql驱动
compile 'mysql:mysql-connector-java'
.....数据库中创建一个表:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(36) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;创建以下类
package com.lckiss.hello;
import mapper.UserMapper;
import model.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* http://localhost:8080/user-detail?id=1
* @param id
* @return
*/ @RequestMapping("user-detail")
public User selectUserById(int id){
return userMapper.selectUserById(id);
}
/**
* http://localhost:8080/insert-user?name=xx
* @param name
* @return
*/ @RequestMapping("insert-user")
public String insertUser(String name){
userMapper.insertUser(name);
return "ok";
}
}一个model
package com.lckiss.model;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}一个mapper
package com.lckiss.mapper;
import model.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
public interface UserMapper {
@Insert("insert into user(name) values(#{name})")
void insertUser(@Param("name") String name);
@Select("select * from user where id=#{id}")
User selectUserById(@Param("id") Integer id);
}在UserController中,我们省略了service层,直接用@Autowired导入了UserMapper进行操作,实际开发中,这样肯定是不允许的,这里只是演示。
最后在App.java文件中加入
@EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.lckiss.hello") //这行是新增的 @MapperScan(basePackages = "com.lckiss.mapper")
完成后重启服务器,尝试先插入一条数据:
http://localhost:8080/insert-user?name=xx
再查询该数据:
http://localhost:8080/user-detail?id=1
待续
源代码:https://github.com/Anr-C/SpringBoot
简单介绍到此,更多请查看:使用IDEA创建一个简单的SpringBoot项目(二)
本站由以下主机服务商提供服务支持:
0条评论